Osteoarthritis (arthrosis deformans national title - salts) is a chronic joint disease, which is degenerative-dystrophic character, which is the destruction of articular cartilage, the capsule of the joint, deformity of the bone.
The key role of the environment, that arthritis is a group of diseases of the joints, of different origin mechanisms and close. The most common knee arthritis of the large joints:
- deforming arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis),
- deforming arthrosis of the hip joint (coxarthrosis)
- as well as osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint.
This difficulty is the most arthritis.
Osteoarthritis of the small joints are less common. More often deforming arthrosis of the interphalangeal joints of the hands and metacarpophalangeal joints of the fingers. Patients report pain in the interphalangeal joints, reducing their mobility, the emergence of near the joints of the seals (nodules and Heberden, Bouchard). This form of arthritis is more common in the elderly. Often arthritis of the joints of the legs.
It polyarthrosis, or generalized osteoarthritis, is characterized by lesions of multiple joints.
Osteoarthritis of the joints and the spine - spondylosis - belongs to the group of diseases of the spine, although is similar to other arthritis mechanism of development.
The main clinical symptom of osteoarthritis is pain in the joint, reducing its mobility. Special are determined by the stage of symptoms depend on the osteoarthritis and on the extent of destructive changes of the joint.
Osteoarthritis causes
Osteoarthritis is the primary and shared secondary. Primary (idiopathic) osteoarthritis is the result of disturbance of regenerative processes and increased degeneration of the cartilage in the joint without any abnormalities throughout the body. Secondary osteoarthritis as a result occur in other pathological processes in the body, or already in external damaged effect on the joint of the partial destruction of the articular surfaces.
Often traumatic osteoarthritis has been diagnosed in young patients. And patients, parents are not always possible to draw a clear line in the primary, and between secondary osteoarthritis.
Although not the exact cause of arthritis of the void to determine the factors that affect its emergence and development is well known.
You can select the following types of reasons to promote the primary and secondary deforming arthrosis of the.
The causes of primary osteoarthritis hereditary factors
It turned out the following hereditary diseases that can cause the development of primary osteoarthritis:
- genetic disorders of cartilage tissue of the joint leading to its rapid destruction;
- congenital malformations of the musculoskeletal system (joint hypermobility, dysplasia, flat feet, etc.), that causes trauma to the individual parts of the cartilage tissue and, consequently, the onset of osteoarthritis.
It was also the key role of the environment, that the deforming arthrosis of the interphalangeal joints of the upper limbs is found predominantly in women and it has inherited the woman through the line.
Causes of secondary osteoarthritis
Secondary osteoarthritis is the result of damage to the joint. Injuries These can be caused by many different factors.
- Mechanical damage to the joints. This group includes a variety of factors, joint injuries, intraarticular fractures, which affect the structure of the connection. The same result is obtained by continuous micro-trauma to joints by excessive permanent loads, both static and dynamic (eg. athletes). And Also overload injuries of the joints causes obesity.
Another factor, which has a negative effect on the joints (especially the hip) is incorrect posture.
The structure of the joint can also interfere with surgery. - Diseases of the joints. Osteoarthritis can be the result of inflammatory joint diseases (acute and chronic arthritis, arthritis, primary aseptic necrosis of bone, etc.)
- Metabolic disorders, endocrine diseases, lack of minerals in the body. Various disorders of metabolism, deficiency of calcium, phosphorus and other minerals, vitamins and cause trace elements of configuration changes and cartilage, bone, synovial fluid, leading to disruption of the repair and the processes of gradual destruction of the whole.
- Autoimmune diseases (gout, chondrocalcinosis, hemochromatosis, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis), hormonal disorders, estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal women cause the tissues of the joints changes and their gradual destruction.
- Vascular disease (atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, obliterating endarteritis, varicose disease), and lack of exercise cause poor blood circulation in periarticular tissues, poor blood circulation in the tissues of the joint leads to degenerative changes.
The mechanism of the development of osteoarthritis
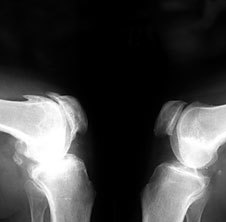
The development of osteoarthritis begins the cartilage loss. It is believed that at the beginning there is a violation of blood circulation in the capillaries Podhradie layer of the periosteum. As the power of cartilage is due to the receipt of nutrients in the synovial fluid and adjacent bone tissues, blood circulation cause the cartilage gradually loses its elasticity, becomes thinner, it cracks, smoothness of the articular surfaces is disturbed, reduces joint the amount of fluid, which provides a sliding connection. The result is pain and crunching when moving. The width of the joint space is gradually reduced, edges formed by the articular surface of the bone spikes-osteophytes.
Eventually, the joint becomes deformed, the amplitude of create is reduced. So develop involutive osteoarthritis is associated with aging. The development of this form of osteoarthritis usually be paid gradually over many years.
Other forms of arthritis of large joints, for example, post-traumatic, post-infectious, metabolic, intoxication is a slightly different mechanism of development, but the result of the same changes is common.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis the joints. Step ny-the degree of osteoarthritis
"Classic" is the classification and based on the osteoarthritis clinical x-ray features. Accordingly there are three stages of disease development. It corresponds to the classification according to the degree of capacity retention, the difference between the 3 ° of osteoarthritis:
- I degree of osteoarthritis - a disease does not prevent the implementation of this work, although yes will do it
- II degree of osteoarthritis - a disease that prevents the execution of the work
- Grade III osteoarthritis of the injury.
Let us consider the clinical symptoms and signs of osteoarthritis at all stages
Osteoarthritis of 1 degree (the initial stage of arthrosis)
In the early stages of the disease in the morning, after a rest, marked stiffness, difficulty of movement in the joints, which gradually paid some time after the beginning of the movement. There may be some restrictions on the connection. At times the "start-up" pain (the pain, you move the kun after a long stay at rest). Sharp movements in the joint tingling, but I don't. The pain is osteoarthritis appears at this stage pointless when significant stress and long-term, subsides after rest. At rest, a light load and there is no pain. At this stage of the disease, patients rarely go to the doctor.
X-ray of osteoarthritis of 1 degree, significant changes in the context are not visible, can sometimes be a little seen with osteophytes on the edges of the joint, the joint space is slightly narrowed.
Osteoarthritis of the 2 ° (second stage osteoarthritis)
With the further development of osteoarthritis the pain is significant, becomes acute. Separate crunching in the context view of all movements, the key role of environmental restrictions in the joints (contracture), functional shortening of the limbs, disorders of the biomechanics of the movement, but mobility is still maintained. This stage is characterized by a significant increase in starting pains, acute and are prolonged. Under the influence of daily physical activity will constant fatigue, feeling the pressure of the affected joints, there is a so-called "mechanical pain", caused by the decline in the ground handling services catering to the ability of the cartilage tissue.
Destruction are common quite significant, the joints have already started to partially change its shape.
X-ray-osteophytes visible view, joint space narrowing of 2-3 times compared to the norm, the disease is not subchondral bone and the formation of cystic cavities in the growth plate area.
Osteoarthritis of degree 2 is characterized by a capacity reduction, the inability to perform certain actions.
Osteoarthritis grade 3 (the third stage of osteoarthritis)
Osteoarthritis grade 3 severe, advanced disease. At this stage is:
- a significant deformity of the joint (due to growth and bone accumulation of fluid in the articular cavity);
- the sharp restriction of movements, which should in vain oscillation;
- a sharp pain, not in vain, when the moves, but also complete rest - the constant pain associated with reflex spasm of the nearby muscles, as well as to develop reactive arthritis;
- inflammation of the joints
- the sensitivity of joints to weather changes.
- the muscles around the knees and spasmatic atrophied;
The axis of the limb is deformed, considerably varus valgus, or curvature of the legs (i.e. in the form of the letter "O" or "X").
Radiographic osteoarthritis grade 3 is almost complete disappearance of joint space, severe deformity of the articular surfaces, there are several marginal osteophytes. To determine the Vertical and joint mice calcification paraartikulyarnye tissues.
Year 3. the degree of advanced disease, often it has already caused permanent injury. Occurs in the following ways:
- the pain is constant and walking painful, especially skiing climbing and stairs can be an ordeal for the patient;
- a loud crunching sound all the movements, very audible to others;
- deformation of joints strongly expressed, the child is restricted to no avail a small amplitude, or even impossible;
The pictures show destruction of the joint structures (ligaments, meniscus ny), and complete wear of the cartilage of the disease and the signs (change the function of organs and structures of the connective tissue).
Osteoarthritis 4 °
The complete destruction of the state of the joint osteoarthritis, when joint training completely stopped several point - 4 degrees of osteoarthritis. There is the so-called "joint blockade" - an acute pain, which is not possible even with limited patient movement in the joint. The fourth degree of osteoarthritis is accompanied by unbearable pain in the joints, which can not be removed even with strong pain medications, and activity therapy intensive. Possible total ankylosis (fusion of joint) or newartriot (the formation of a false joint between the displaced ends of the bones). The independent movement in both cases is almost impossible.
The picture shows the rough surface soslanovna disease, who have severe cystic enlightenment, the accretion connect to the bones of common area space. The development of the disease almost always at this stage means a disability, which can prevent unnecessary implantation of artificial prosthetic joint.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
Treatment of osteoarthritis the early stages of the disease
Better start to deal with osteoarthritis as soon as possible, at the first signs of a crunch in joints, difficulty in movement. At this stage, useful products - chondroprotectors, which improve the structure of cartilage, vitamin and mineral complexes.
What is important is the therapeutic exercise, proper and dietary preventive measures. The key role of the environment, the prevention of osteoarthritis is very important to prevent exacerbation of the disease.
In the treatment of arthritis 2 - 3 °
Although fully cured arthrosis of 2-3 ° is impossible, but can slow down development significantly. Treatment of osteoarthritis in this stage includes the following steps:
- to remove or reduce pain
- to relieve inflammation of the joint.
- cartilage and improves regeneration slow down the degenerative processes that.
In the acute stage for the treatment of osteoarthritis begins with pain relief. For this purpose, non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (A), pain meds. Possible intraarticular injections of corticosteroids. It is necessary to reduce the load on the joint, you can't walk or stand, lift heavy objects.
After the withdrawal of acute pain, the main task is to ensure, to the extent possible, activation of regenerative processes and a common periarticular tissues: improves blood circulation, increases metabolism, elimination of inflammatory processes. Demonstrated chondroprotectors, vasodilator drugs, as well as remedial gymnastics and occupational therapy.
Osteoarthritis 4 °
At this stage the disease is common almost completely destroyed. In this case, the vain one option - surgery and joint replacement the diseased, which is the prosthesis. The implant significantly improves the mobility of the joint, allowing the patient to continue an active life, at least, get rid of the pain.












































